

Plumbing is indispensable in maintaining the functionality of modern society’s infrastructures. Professionals in this trade install, repair, and maintain systems that ensure the seamless flow of water and gas into homes and businesses and the safe disposal of waste. Plumbing is a vocation demanding precision, problem-solving skills, and specialized tools to perform tasks efficiently.
Overview of the Plumbing Profession
Plumbing professionals handle many tasks, from fixing leaky faucets to installing extensive piping networks for new constructions. Their expertise covers residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, each presenting unique challenges requiring technical skills and practical experience. Training and apprenticeship are crucial to gaining proficiency in this complex domain, with rigorous safety protocols and regulations to follow.
Importance of Having the Right Tools
Success in plumbing hinges on the availability and utilization of proper tools. Plumbers rely on an arsenal of equipment to diagnose issues, execute repairs, and ensure the longevity and safety of plumbing systems. Each tool serves a distinct purpose, from gripping and tightening components to cutting and shaping pipes. Furthermore, the correct tool not only enhances the efficiency of a task but also ensures the protection of both the plumber and the property they work on. Investing in high-quality tools reduces the likelihood of unexpected malfunctions and contributes to the overall reputation of the plumbing professional.
Changes and Advances in Plumbing Tools for 2024
In 2024, advancements in technology have transformed the plumbing industry’s toolset. Modern tools now incorporate innovative technology, providing plumbers with data-assisted diagnostics and precision-based solutions. These advancements reflect a transition towards more efficient, durable, and ergonomic designs, allowing plumbers to undertake complex tasks more efficiently. The year’s notable changes include:
- The integration of wireless connectivity in inspection cameras.
- The increased use of press fitting tools for secure pipe connections.
- The rise of modular tool systems for enhanced portability and convenience on the job.
With these refined implements, plumbing professionals are better equipped to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving industry, signifying an era that appreciates the interplay between craftsmanship and innovation.
Essential Hand Tools for Everyday Plumbing Tasks
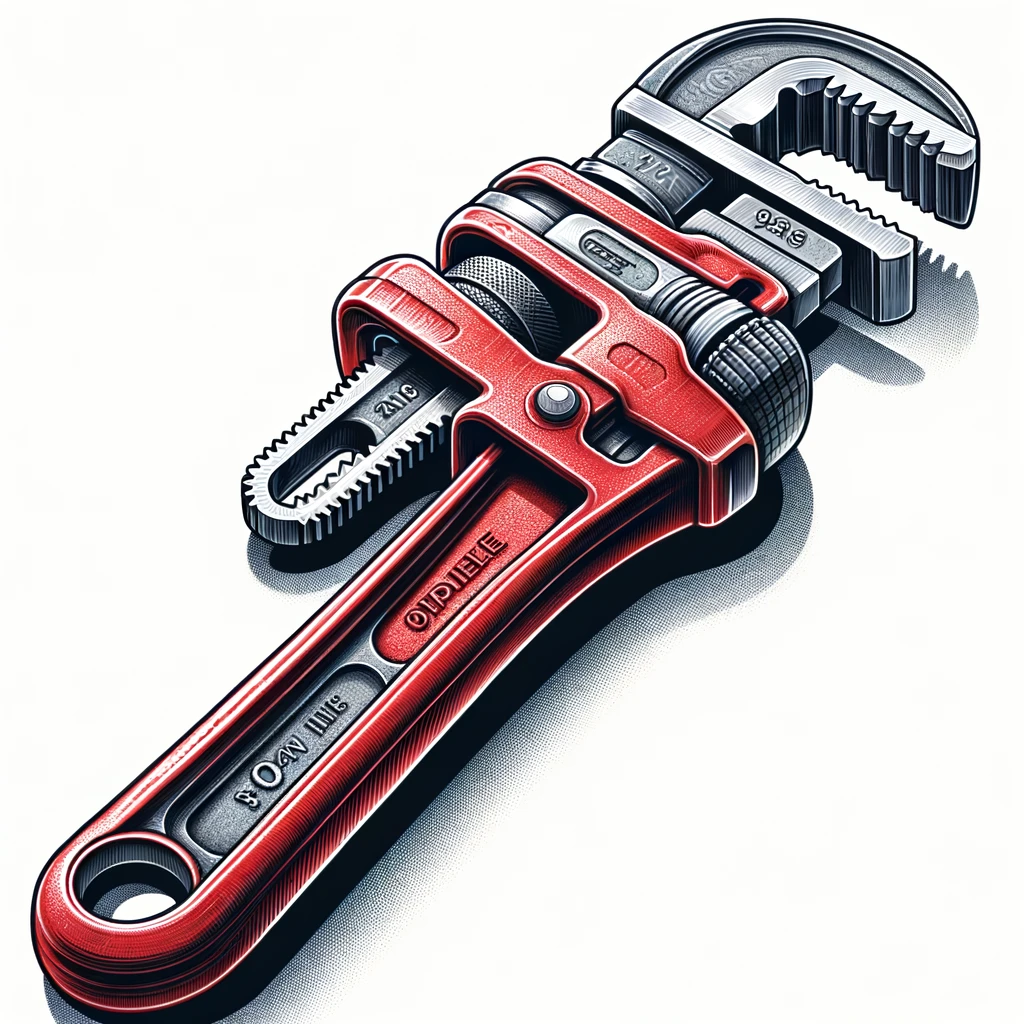

Pipe Wrenches
Pipe wrenches are symbolic tools for plumbers. They are quintessential for grasping and turning pipes due to their sturdy construction and serrated jaws, which grip tightly around pipe surfaces. They come in different sizes and are essential for working on metal pipes, fittings, and connections. The larger wrenches provide more leverage for stubborn pipes. A plumber often requires at least two pipe wrenches, one for turning and the other to steady the pipe. Significantly, a plumber uses these wrenches carefully to prevent damage to the finish on fittings.
Adjustable Wrenches
Adjustable wrenches feature prominently in a plumber’s toolkit, providing versatility with their movable jaws to fit various nut and bolt sizes. Typically, they come into play for securing or loosening hexagonal compression fittings and supply lines. The smooth jaws of adjustable wrenches are ideal for work on fixtures and supply lines as they minimize damage to the finish. Given their utility across a wide span of sizes, these wrenches eliminate the need for a vast collection of fixed-size wrenches, making them an innovative, space-saving solution for professionals.
Locking Pliers
Locking pliers is invaluable in any plumage task where a stable grip is essential, such as clamping onto objects, twisting wires for safety, or tightening bolts. Their adjustable wrench-like mechanism and ability to lock in place distinguish them from regular pliers, augmenting a plumber’s ability to hold objects securely without continuous manual pressure. The enhanced grip provided by locking pliers is beneficial for their traditional uses, and when a handle on a tool has broken, it turns them into temporary fixes.
Screwdrivers and Hex Key Sets
With its simple yet indispensable design, the screwdriver is vital for many plumbing-related tasks. Plumbers should possess a collection of flat-head and Phillips-head screwdrivers in various sizes for tasks such as disassembling faucets or adjusting appliances’ components. Advanced designs now feature interchangeable heads, which add utility and convenience to the quintessential screwdriver.
Complementing screwdrivers, hex key sets (also known as Allen wrenches) accommodate the operation of hexagonal socket screws frequently encountered in plumbing fixtures. With the prevalent use of these screw types in modern hardware, a set of these L-shaped wrenches becomes critically essential for assembly and disassembly processes. Hex key sets usually come in various sizes, ensuring a plumber can address bolts of varying dimensions precisely and efficiently.
Measuring and Precision Tools
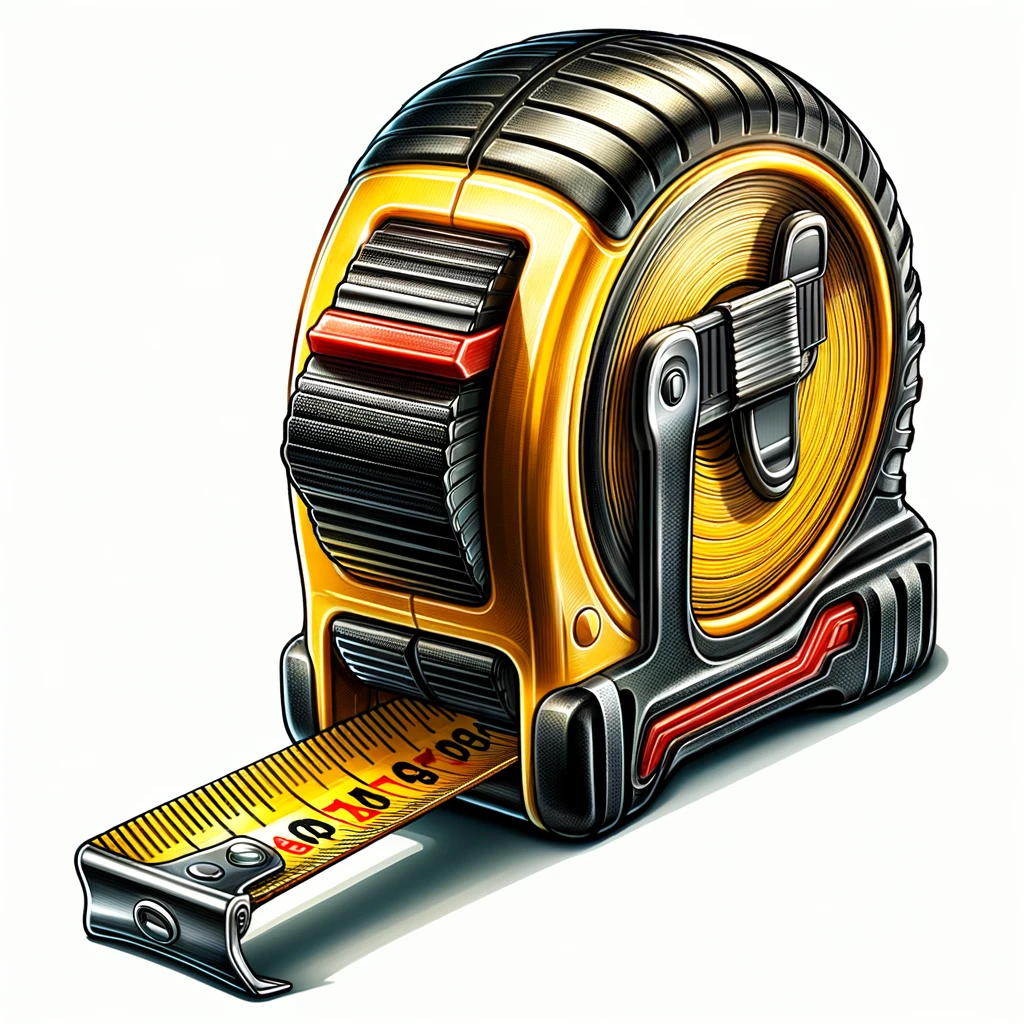

In plumbing, precision is not just a preference; it’s a requirement. In 2024, plumbers must understand the instruments that achieve exact measurements to ensure successful installations and repairs. These tools ensure pipes fit accurately, leaks are avoidable, and plumbing systems remain intact. In this regard, the essential measuring and precision tools enlisted are non-negotiable for any plumber aiming to maintain a professional standard.
Tape Measure and Rulers
The tape measure remains an indispensable tool for any plumber. It provides the ability to quickly and efficiently gauge distances and lengths of pipes, spaces for installations, and the dimensions of fittings. A retractable, lockable tape measure, resilient to the daily rigors of a plumber’s workload, is a quintessential item in the toolbox. With the evolution of technology, digital tape measures that display readings directly onto a digital screen have also become prevalent. Moreover, rigid rulers, often made from stainless steel, are vital for smaller measurements and when rigid straight lengths are required for accuracy.
Level
Plumbers understand that the correctness of an angle or slope in pipework can mean the difference between a well-functioning system and one plagued by issues. For this reason, a level is a critical tool to ensure pipework and fixtures are accurately aligned and balanced. Torpedo levels, typically compact and easy to maneuver in tight spaces, have magnetic edges for stability and clear vials filled with a colored liquid to indicate levelness. Some newer models include laser technology offering a cross-check vial and a digital readout for precise alignments, enhancing efficiency in setting the correct gradients for proper drainage and system functioning.
Calipers and Micrometers
Regarding intricate measurements, calipers and micrometers are the go-to instruments. These tools are vital for gauging the external and internal dimensions of pipes, fittings, and seals. Calipers, which can be digital or manual, allow plumbers to capture accurate measurements down to fractions of a millimeter, which is essential for ensuring the tightness of fit and preventing leaks. Digital calipers, with their on-screen readings, provide a quick and precise measurement, reducing the margin of error.
Micrometers take precision a step further, offering even more exact readings. They are typically used when extreme accuracy is needed, such as the threading of pipes or when measuring the thickness of materials.
Together, these tools form the cornerstone of any plumber’s precision toolset. Their use improves the quality of work and reflects a plumber’s commitment to the trade and attention to detail. Possession and adept handling of these measuring and precision tools set the ground for impeccable plumbing practices and uphold service standards in line with the industry’s evolving expectations.
Cutting and Shaping Tools
As the plumbing industry evolves, professionals must arm themselves with cutting and shaping tools that combine precision, efficiency, and adaptability. The right tools ease the day-to-day tasks of cutting and preparing pipes and ensure a high-quality finish synonymous with professional plumbing work.
Tube and Pipe Cutters
Tube and pipe cutters are paramount for any plumber seeking to make clean and precise cuts in various materials. Modern cutters are engineered to handle a range of materials, from the most common PVC and PEX to copper and stainless steel. Plumbers must opt for cutters designed for the specific materials they frequently work with to ensure a smooth cut that minimizes the risk of pipe damage.
Advancements in tube and pipe cutter designs include ratcheting cutters and rotary cutting tools that are ergonomically crafted to reduce hand fatigue. These cutters often come equipped with sharp, replaceable blades that can slice through pipe materials with minimal burr formation, allowing for a more seamless connection during installations. In addition to the hand tools, powered pipe cutters have increased in popularity, featuring battery-powered operations that can notably accelerate the cutting process for large-scale projects.
Hacksaws
Hacksaws remain in the plumber’s toolkit due to their versatility and ability to cut through various materials, including metal pipes, brackets, and bolts. Selecting a hacksaw with a robust frame and adjustable tension settings can improve the accuracy and ease of cutting through different thicknesses and materials. High-grade, fine-toothed blades are recommended for cutting metal pipes, as they create a cleaner edge, which is integral to a well-fitted joint.
While traditional hacksaws remain valuable, there has been a rise in the use of compact, tight-access saws. These saws are specially constructed to operate in constrained spaces, often in plumbing work environments. The ability to change blades quickly and safely is another factor that plumbers consider, which allows them to adapt to different materials and scenarios encountered on the job.
Deburring Tools
Preparing the pipe for installation or welding after executing a cut is critically essential. Deburring tools are designed to remove any residual material or sharp edges left on metal or plastic pipes after cutting. They are available in various forms, from simple handheld models to more sophisticated attachments that can be used with power drills for speedier operation.
Quality deburring tools are vital to ensure the longevity and integrity of pipe connections. A well-deburred edge helps avoid leaks and protects seals and gaskets from damage during installation. The industry has seen an emergence of multifunctional deburring tools that not only clean the outside edge but simultaneously ream the inside of the pipe, which is essential for ensuring a full flow of liquids or gases through the pipeline system.
High-quality deburring tools now often feature swivel heads that adjust to the pipe’s contour, allowing for a uniform finish around the circumference. This advancement is especially beneficial when working with pipes of different diameters and materials, providing plumbers with a one-tool solution for multiple applications.
In the rapidly advancing world of plumbing, professionals must stay informed about the latest tool innovations that can drive their efficiency and the quality of their work. Cutting and shaping tools remain an essential component of any plumber’s inventory, with modern advancements tailored to meet plumbing tasks’ diverse and demanding nature in 2024 and beyond.
Pipe and Tube Bending Tools
Pipe and tube bending tools are essential in a professional plumber’s arsenal. They shape plumbing pipes to meet the requirements of complex installations where a standard straight pipe cannot fit. Advanced tools have been developed to ensure precision and efficiency, contributing significantly to a plumbing system’s quality and integrity.
Manual Pipe Benders
Manual pipe benders are a staple in plumbing due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They typically come in handheld designs or larger, lever-operated bench-top models. These benders require physical force to create bends but allow for a high degree of control during the bending process. They are best suited for soft materials like copper and thin-walled steel. Quality manual benders feature adjustable guides to align various pipe diameters and bending angles, helping ensure uniformity and accuracy in the bends.
Manufacturers have innovated on materials and designs to reduce the effort required to operate these benders, making them more ergonomic. Some tools include ratcheting mechanisms or longer handles to increase leverage without compromising the precision of the bend. Manual pipe benders do not require electrical power, making them indispensable in remote or confined spaces where portability is critical. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty or industrial-scale work involving persistent thick-walled or large-diameter pipe bending.
Hydraulic Bending Equipment
Hydraulic bending equipment represents the high end of bending technology, characterized by its ability to deliver consistent and substantial force through hydraulic pressure. These tools cater to various pipe materials, including stainless steel and other hard alloys, and can accommodate larger pipe diameters where manual force would not suffice. Hydraulic benders benefit from precise control systems, often digital, that allow plumbers to set exact bending angles and achieve repeatable results for mass-production tasks or specialized projects.
Portable hydraulic benders have been introduced, combining the power of hydraulic systems with the flexibility to operate in various work environments. They typically comprise a hydraulic pump, bending frame, and formers for different pipe sizes. With an emphasis on adaptability, modern hydraulic benders include features such as quick-change tooling systems that reduce downtime and increase productivity.
As the complexity of plumbing systems evolves with modern construction, hydraulic bending tools are becoming more sophisticated with the integration of software that can calculate exact bend sequences and angles required for intricate layouts. They provide real-time feedback and error correction, which minimizes material waste and ensures installation integrity. For plumbers invested in large-scale or industrial contracts, hydraulic benders offer a combination of power, precision, and efficiency that manual tools cannot match, affirming their status as essential in 2024’s plumbing industry.
Plumbers must remain informed about the best practices for using bending tools and adhere to safety standards to prevent pipe damage and personal injury. Manufacturers continue to innovate in the field, emphasizing operator comfort and bend accuracy while expanding the capabilities of manual and hydraulic benders to keep pace with the plumbing industry’s evolving needs.
Advanced Inspection and Diagnostic Tools
The plumbing industry has evolved with the advent of advanced inspection and diagnostic tools that enhance plumbers’ efficiency and accuracy. These tools are vital in diagnosing complex issues within plumbing systems, which can save time and resources for professionals and clients alike.
Inspection Cameras
Inspection cameras, commonly known as endoscopes or borescopes, have become an indispensable tool for modern plumbers. These cameras are designed to be maneuvered through pipes, allowing for a visual examination of internal conditions without destructive measures. The high-definition image capabilities and flexible form factor enable plumbers to identify obstructions, cracks, and other issues that may not be visible outside. Recent models are often equipped with LED lighting, providing clear illumination in dark environments, and can capture still images or video footage for further analysis and documentation.
Pressure Gauge and Test Plugs
Measuring water pressure in a plumbing system is essential for maintaining optimal function and identifying potential problems. Pressure gauges accurately read the system’s pressure, which is necessary for diagnosing issues such as high-pressure levels that can lead to pipe damage or low pressure that could indicate leaks. In combination with test plugs, professionals can isolate sections of the plumbing to test each segment individually, ensuring meticulous attention to detail in the diagnostic process. These tools are fundamental in validating the integrity of a system after repairs have been completed.
Leak Detection Equipment
Leak detection equipment is critical in locating and addressing hidden leaks, one of the most challenging tasks for plumbers. These devices can detect leaks not apparent to the naked eye or accessible without significant excavation. Advanced acoustic devices can hear water escaping from pipes buried in walls or underground, differentiating it from noise pollution. Thermal imaging cameras use infrared technology to identify unexpected temperature changes in walls and floors, which can indicate the presence of moisture from concealed leaks. Utilizing leak detection equipment avoids unnecessary property damage and saves resources by pinpointing water loss sources precisely.
These modern inspection and diagnostic tools embody the plumbing industry’s technological advancement, allowing plumbers to provide precise, less invasive, and more reliable services. Understanding and utilizing these tools reflect high-level expertise and professionalism, ensuring plumbing systems operate safely and efficiently. Integrating such equipment into daily plumbing practices demonstrates a commitment to quality and a forward-thinking approach, which benefits both the trade and the customer.
Drain and Sewer Cleaning Equipment
Proficiency in drain and sewer maintenance is a foundational skill set for plumbers. The dynamic nature of plumbing systems requires a selection of versatile tools specifically designed to address clogged and blocked pipes efficiently. Modern plumbing practices have sharpened the focus on equipment that solves the immediate problem and preserves the integrity of the plumbing infrastructure over time.
Hand Augers and Plungers
Hand drills, often called plumber’s snakes, are critical in the plumber’s toolkit. They comprise a flexible metal cable with a corkscrew-like tip designed to navigate tight bends and dislodge stubborn blockages in pipes and drains. Manual operation provides plumbers with tactile feedback, allowing them to sense the severity and nature of the clog and adapt their technique accordingly. Hand drills are particularly effective in residential settings, where common blockages are often caused by hair, soap residue, and small objects.
Plungers are the first line of defense against simple clogs. They work on creating a vacuum seal around the drain opening and using pressure to dislodge obstructions. A plunger’s effectiveness is predicated on the quality of the seal it forms and the plumber’s skill in using it to generate enough pressure to clear the blockage. Plungers’ simplicity and non-invasive nature make them indispensable for day-to-day plumbing tasks.
Drain Snakes and Hydro-Jetters
Drain snakes, or motorized drain augers, are an evolution of hand augers designed to tackle more challenging blockages. These electric or battery-operated devices provide enhanced power and reach, allowing plumbers to clear obstructions further along the sewer line without excessive manual labor. Drain snakes come with varying cable lengths and thicknesses, allowing plumbers to address different clogs across multiple environments—from residential bathrooms to commercial kitchens.
Hydro-jetters take a different approach to drain cleaning, utilizing high-pressure water streams to break apart blockages and flush out debris from the pipes. These tools are particularly effective in removing build-ups of grease, minerals, and other residues that adhere to the interior walls of pipes. Since they only use water, hydro-jetters are a safe and eco-friendly option, eliminating the need for harsh chemicals. They are essential for maintaining large-scale sewage systems and are integral to performing preventive maintenance. The precision of hydro-jetters allows plumbers to clean pipes thoroughly, thus minimizing the risk of recurrent clogs.
Equipped with these robust and sophisticated drain and sewer cleaning tools, plumbers in 2024 are well-prepared to ensure the optimal functioning of essential infrastructure. By leveraging these tools, plumbers contribute to the longevity of plumbing systems and the environment’s overall health. As these tools evolve with technological advancements, their contributions towards efficient and sustainable plumbing practices become even more pronounced.
Joining and Sealing Tools

Proper joining and sealing in plumbing are crucial to ensuring leak-proof connections and overall system integrity. Plumbers, therefore, rely on various tools and materials that facilitate this aspect of the trade. The complexity and precision required in joining and sealing applications necessitate tools and compounds that offer reliability and efficiency suited to the evolving materials and standards of 2024.
Soldering Torches and Brazing Equipment
Soldering torches and brazing equipment are fundamental for creating enduring metal pipe connections. Skilled plumbers use high-temperature torches to melt solder or filler metal, which, upon cooling, forms a strong bond between the metal pieces. The selection of a soldering torch or brazing equipment requires consideration of factors such as temperature control, ease of use, and material compatibility.
Modern soldering torches have evolved to provide better thermal efficiency and safer operation. Features like adjustable flame controls, ergonomic design, and enhanced safety mechanisms are typical. When it comes to brazing, the choice of filler material is pivotal for structural integrity, and it must align with the specific metal compositions involved in the joint.
Thread Sealing Tape and Compounds
Preventing leaks in threaded pipe connections is paramount, and that’s where thread-sealing tape and compounds come into play. Thread sealing tape, often known as plumber’s or PTFE tape, is a ubiquitous choice for its ease of application and effectiveness in filling the minute grooves between threads to prevent leaks.
In addition to the tape, various thread-sealing compounds or pipe dopes are used to ensure a watertight seal. These sealants are designed to remain pliable, fill potential gaps, and prevent corrosion. Compounds may vary based on the types of fluids being conveyed, temperature ranges, and the material of the pipes to ensure longevity and avoid chemical incompatibility.
Press Fitting Tools
Press fitting tools are revolutionizing pipe connection techniques, offering a flameless alternative to traditional soldering and brazing. Using mechanical force, these tools securely join pipes and fittings with press-connect ends by crimping the metal fitting onto the pipe, effectively making the connection leak-proof.
Press fitting tools save installation time and reduce the risk of fire-related hazards. Additionally, they are suited for use on various pipe materials, including copper, stainless steel, and PEX. As new materials and designs surface in 2024, the adaptability of press fitting tools continues to be a consideration for their inclusion in every plumber’s toolkit.
Such tools include intelligent features like press cycle monitoring and jaw alignment indicators, ensuring each joint is completed precisely. Reliable and consistent results are paramount, and today’s versions often include data logging capabilities to track and assure the quality of each join.
Updated joining and sealing tools are integral for modern plumbers to adapt to industry advancements and maintain the integrity of plumbing systems. Soldering torches, brazing equipment, thread sealing tape, compounds, and press fitting tools represent the essential arsenal for professionals who demand excellence and efficiency in their craft. As plumbing materials and standards continue to evolve, these tools will remain indispensable, evolving to meet the demands of the trade in 2024 and beyond.
Safety Equipment and Accessories

Personal Protective Gear
Plumber’s safety is paramount when they confront an array of hazardous environments. Hence, the selection of personal protective gear is critical. Durable gloves are the first defense against cuts and abrasions, preferably those with nitrile coatings for waterproofing and chemical resistance. Plumbers often require safety goggles or face shields to protect against flying debris, particularly when cutting or soldering pipes.
Ear protection, such as noise-reducing earmuffs, is essential when operating loud equipment. Coveralls or utility aprons offer an extra layer of security while simultaneously providing pockets for carrying small tools and parts. With the potential for slips and falls, plumbers should equip themselves with slip-resistant shoes. Selecting footwear with protective toe caps can minimize injury from heavy objects. Non-conductive boots are necessary for scenarios involving potential exposure to electrical hazards. Respirators become indispensable in poorly ventilated areas where plumbers might encounter mold, asbestos, or sewer gases. Each gear must adhere to established safety standards, such as those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and appropriate local guidelines.
Portable Lighting
Portable lighting illuminates confined and poorly lit work areas, which is crucial for both quality of work and safety. Plumbers’ lighting tools include headlamps, handheld flashlights, and freestanding work lights.
Headlamps provide hands-free operation, which is essential when a task requires both hands. LED technology has revolutionized portable lighting, offering brighter light with lower energy consumption. Lighting equipment must be waterproof, impact-resistant, and have a long battery life for optimal functionality. Some advanced portable lighting solutions include adjustable light intensity, focus control, and emergency flashing.
Rechargeable work lights with 360-degree lighting offer ample illumination for larger workspaces. Innovations like lights with magnetic bases for easy mounting or motion-sensing capabilities for enhanced user convenience continue to emerge.
Tool Storage Solutions
Plumbers’ efficiency and productivity largely depend on how well they organize their tools and accessories. Tool storage solutions are, therefore, indispensable for protecting, organizing, and transporting plumbing tools.
Plumbers require sturdy tool bags made from heavy-duty fabrics with multiple compartments tailored for standard plumbing tools; for convenience and easy access to tools, rolling tool bags and backpacks equipped with wheels and retractable handles stand out. Those who manage extensive inventories might opt for stackable toolboxes that can be linked to simplify transporting multiple cases. Portable workbenches with integrated storage systems grant additional workspace while keeping tools within reach. For stationary workshops, wall-mounted pegboards and drawer organizers help maintain an orderly setup. Each solution should display characteristics such as durability, flexibility, and water resistance to withstand the challenging conditions of plumbing work. Advancements in tool storage technology have introduced features such as lockable compartments for securing valuable items, corrosion-resistant metal parts, and UV protection for extended outdoor use. Tool tracking systems, with the assistance of intelligent technology, enable plumbers to manage and locate their tools efficiently.
Tool Maintenance and Upkeep
Cleaning Your Tools
Effective tool maintenance for plumbers involves regular cleaning to prevent the accumulation of dirt, grease, and other contaminants that can impair their functionality. Each tool requires specific attention that is aligned with its material and use. For metal tools such as pipe wrenches and plunger heads, a damp cloth with a mild detergent removes grime, while a dry cloth afterward prevents rusting. Tools with intricate mechanisms like telescopic inspection cameras necessitate using compressed air to dislodge debris and specialized cleaning agents designed for electronic components. Proper drying is crucial; residual moisture can lead to corrosion in even stainless steel tools. Plumbers often apply a light lubricant to movable parts to ensure smooth operation. The industry standard dictates avoidance of harsh chemical cleaners that can damage tool surfaces and potentially compromise the integrity of plumbing fixtures when used after that.
Routine Inspection for Wear and Damage
Scheduled inspections ascertain that tools continue to perform at optimal levels and safeguard against the risks associated with tool failure. Visual examination is fundamental; plumbers check for cracks in handles or housing, ensure that cutting blades possess unblemished edges, and verify the structural integrity of cables and connectors on devices like drain snakes and sewer cameras. They evaluate joint movement for signs of stiffness or excessive loosening that could indicate wear or the need for replacement parts. Instruments such as pressure gauges and pipe threaders are tested to ensure accuracy, for even minor discrepancies can lead to significant issues in plumbing systems. Plumbers preemptively replace items before they become liabilities in critical situations by adhering to manufacturer guidelines on the lifespan of tools and components.
Calibration and Adjustments
Among the most critical maintenance duties is the calibration and adjustment of precision instruments. Electronic devices like digital pipe locators require regular calibration to maintain accuracy; this often refers to specific calibration points the manufacturer sets. Manometers and pressure gauges, essential for verifying system pressures, may drift from their accurate readings over time. Thus, they need recalibration to ensure their readings are consistent with pressure values. Adjustments for hand tools such as torque wrenches are necessary to maintain the precise force required for fastening applications. Failure to maintain calibrated specifications not only impairs plumbing work but can also pose safety risks. In calibration maintenance, plumbers frequently rely on certified calibration services or follow detailed, tool-specific procedures to adjust settings in-house, thus ensuring their tools facilitate reliable, high-quality artistry in the field.
A plumber’s toolkit comprises tools that are subject to regular use and, as such, require diligent upkeep to maintain their performance and longevity. Cleaning, inspecting, and calibrating tools are fundamental practices that contribute to successful plumbing repairs and installations while also ensuring the plumber’s safety. Compliance with these maintenance routines serves as a benchmark for professionalism. It contributes to the plumber’s reputation for delivering accurate, efficient, and reliable services.
Upcoming Technological Advancements in Plumbing Tools

Smart Tools and Equipment
Intelligent tools and equipment are game changers in the plumbing industry, providing plumbers with unprecedented efficiency and precision. These innovations encompass a range of devices, from pipe inspection cameras with high-resolution imaging to sensor-based wrenches that alert users to optimal torque levels. Advanced leak detection systems also use sound technology to pinpoint the exact location of leaks, even through walls and concrete, reducing the need for invasive inspections.
Moreover, intelligent cutters and joining tools with Bluetooth connectivity can automatically adjust settings based on the material and dimensions of the pipework, ensuring perfect cuts and secure joints every time. The data these tools collect are not merely for immediate use but can be stored and analyzed to predict tool maintenance and enhance job planning. For instance, thermal imaging cameras have been developed to enable plumbers to see through structures for potential blockages or leaks, with images and readings that can be directly sent to clients or team members.
Technological advancements also lead to tools that enhance safety and ergonomics. Electrically powered tools with intelligent sensors can reduce strain on the plumber’s body and are designed to shut off in unsafe conditions, mitigating the risk of accidents. These smart tools are revolutionizing how plumbing tasks are performed and how plumbers interact with everyday tools.
Integration with Mobile and Cloud-Based Applications
Integrating plumbing tools with mobile and cloud-based applications is rapidly transforming the landscape. Applications now exist that work in tandem with various tools, enhancing their functionality and providing plumbers with a centralized platform for job management. These applications can store customer information, job history, invoicing, and real-time data from intelligent plumbing tools, creating a seamless workflow for plumbing professionals.
Cloud-based software can track tool performance and maintenance schedules, ensuring tools are in top working condition and minimizing downtime. With mobile integration, plumbers receive immediate notifications regarding potential equipment issues on their smartphones or tablets, allowing prompt action, such as ordering parts or scheduling repairs.
Additionally, inventory management is simplified as RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags on tools enable real-time tracking, ensuring that plumbers have all necessary equipment before heading to a job site. GPS functionality enhances this, providing the most efficient routes to a job, considering real-time traffic conditions.
Customer engagement has also improved, as plumbing businesses can update customers on appointments, job progress, and digital reports through their customer-facing apps. This level of customer service not only boosts satisfaction but also aids in building trust and promoting business. Combining cloud computing and mobile apps leads to more intelligent business decisions based on actionable insights derived from data analytics on tool usage patterns and job outcomes.
The plumbing industry is experiencing a technological revolution. Intelligent tools and equipment, paired with mobile and cloud integration, are changing the landscape of plumbing work. These advancements contribute to more accurate diagnostics, efficient processes, enhanced safety, and higher customer satisfaction. In 2024, plumbers must stay abreast of these technologies to remain competitive and provide the highest level of service.
Building a Comprehensive Plumbing Toolkit
Plumbers must curate their toolkits with specialized equipment and general hardware to handle various challenges. Essential tools range from pipe wrenches and plungers to more sophisticated devices like inspection cameras. A well-rounded toolbox can differentiate between a simple fix and a prolonged project. Every plumber’s toolkit should evolve constantly, embracing new technologies and retiring outdated methods. A comprehensive plumbing toolkit significantly ensures a plumber is ready for any job, enhancing efficiency, safety, and the quality of repairs or installations.
Selecting Quality Over Quantity
A seasoned plumber knows an overflowing toolbox can be less practical than a carefully selected set. High-quality tools, while sometimes more costly, tend to have a longer lifespan and provide reliability during critical tasks. Quality tools often offer better grip, more accurate measurements, and enduring materials resistant to the wear and tear of regular use. For instance, a pipe cutter made with superior steel will cut more precisely, resist corrosion, and maintain its edge through countless cuts. It is thus critical to prioritize procuring tools that can withstand the rigorous demands of the plumbing profession.
Investing in Multi-Function Tools
Multi-function tools are gaining prominence in the plumbing industry, representing a synthesis of versatility and space-saving design. A tool that combines the functions of several others can reduce the weight and complexity of a plumber’s toolkit, allowing for a more organized and accessible workspace, whether on-site or in transit. A multi-head wrench set, adaptable pipe shears, or an all-in-one soldering station are examples where a single purchase can prevent the need for multiple individual tools. The investment made in these multi-purpose tools can improve overall productivity and shorten the time spent on each job.
Continuous Learning and Tool Upgrades
The world of plumbing is in constant flux, with innovations surfacing routinely. Continuous learning is fundamental to navigating these changes. Plumbers must stay informed about new methods and products and continually reassess and upgrade their toolkits. This may involve embracing digital tools, such as apps that provide instant access to plumbing codes or user-friendly digital gauges that offer precise measurements. Trade shows, plumbing courses, and online forums can be invaluable resources for plumbers looking to keep their toolkits state-of-the-art. Upgrades are about adding new tools and replacing older ones with more efficient, ergonomic, and safer models as they become available.
Committing to ongoing education and tool refinement ensures plumbers maintain a competitive edge and provide the highest standard of service.